Table of Contents
Though seemingly simple, proper home waste management can help combat climate change. Without realizing it, every day we produce various types of waste, from food scraps to plastic packaging.
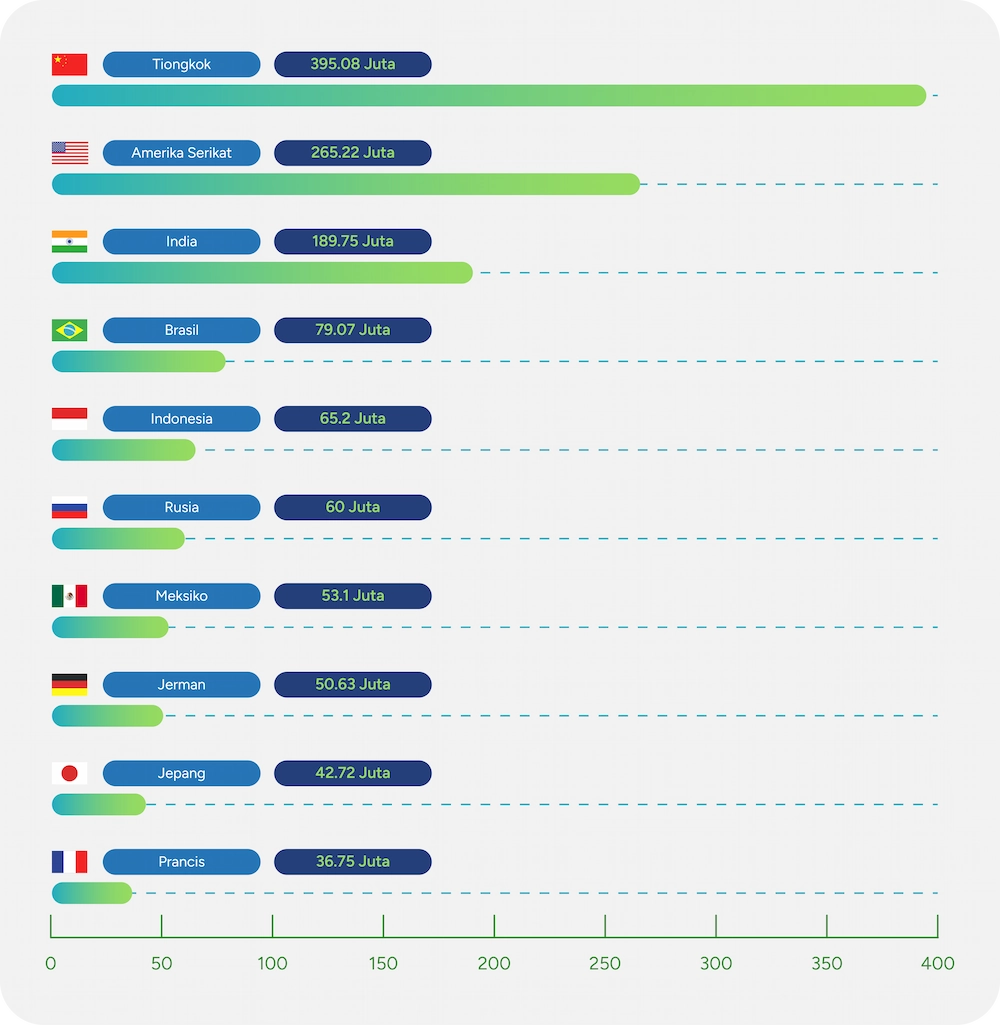
Based on data from Databoks, Indonesia was the 5th largest waste producer in the world in 2020.
Furthermore, according to data from the National Waste Management Information System (SIPSN), Indonesia generated 38.26 million tons of waste in 2023.
If left unchecked, this pile of waste will not only pollute the environment but could also contribute to global warming.
To take necessary measures in waste management, we should be aware of types of waste based on their classifications, namely nature, form, and origin. Let’s learn about it in the explanation below!
What Is Waste?
According to UU No. 18/2008 on Pengelolaan Sampah (Waste Management), waste is the residue of daily human activities or natural processes.
In other words, waste is leftover material from human or natural activities without any use value. Most waste goes to the trash bin or the dump, which may cause a massive pileup. Improper waste disposal or management can hurt the environment and negatively impact human health.
Types of Waste Based on Their Nature
Waste can be categorized based on its nature. It means differentiating waste that can decompose naturally or not. Here’s the explanation:
Organic Waste
What is organic waste? Organic waste is a waste that can be decomposed naturally by microorganisms. Common examples include food scraps, pieces of fruit, vegetables, or leaves. It generally breaks down easily and can be recycled into compost, which helps nurture plants.
Read also: Beware! Don’t Underestimate This Waste in Your Home!
Inorganic Waste
Unlike organic waste, inorganic waste is difficult to decompose naturally. Several examples are plastic, glass, and metal. Inorganic waste takes a long time to decompose, even up to hundreds of years.
Therefore, this waste often requires specific processing techniques so it doesn’t pollute the environment.
Hazardous and Toxic Waste (B3)
B3 waste is a type of waste that contains hazardous and toxic substances. Some examples include medical waste, such as syringes, masks, electronic waste, and chemicals.
Hazardous waste requires special handling. The process requires careful management, or it will potentially damage the environment and threaten health.
Types of Waste Based on Its Form
Waste can also be categorized based on its physical form: solid or liquid. Each of these types requires different handling. Here is the explanation:
Solid Waste
Solid waste has a clear physical form, such as plastic, paper, glass, and metal. It often comes from household, office, and industrial activities. Usually, solid waste is collected in bins and transported for recycling or disposal to landfills.
Liquid Waste
Liquid waste, commonly known as household waste, comes from various human activities, such as laundry, industrial activities, and water from the bathroom.
Improper management can cause liquid waste to pollute the surrounding water and soil. The waste disposal or management requires special care so it doesn’t interfere with environmental safety.
Read also: Various Liquid Waste That’s Surprisingly Beneficial – What Are They?
Types of Waste Based on Their Origins
Apart from its nature and form, waste can also be distinguished based on its origin. These types of waste indicate where the waste comes from. The explanation is as follows:
Natural Waste
Natural waste comes from nature, such as fallen leaves, broken tree branches, and rotting fruit on the ground. This waste is usually self-degradable with no negative environmental impact, as it is part of a natural cycle.
Human Waste
Human waste comes from human digestive products, including urine and feces. Without proper management, this waste can become a concern and end up causing sickness, like diarrhea and typhoid. Such a health problem can happen due to the accumulation of viruses and bacteria in the drains.
Consumer Waste
Consumer waste comes from daily human consumption needs, such as food wrappers, beverage cans, and other product packaging. This waste usually consists of inorganic waste that is difficult to decompose and can pollute the environment if not processed with standardized procedures.
Industrial Waste
Industrial waste comes from the production process in factories or industrial activities. This type of waste has solid or liquid forms containing hazardous materials.
Industrial waste often requires significant management procedures to prevent environmental pollution because it contains many hazardous materials.
That’s the end of the explanation regarding the types of waste. Remember, managing waste is not just about disposing of it but also understanding the impact of each waste in our daily lives.
By sorting your waste at home, you can help keep the environment clean while helping to reduce the effects of climate change.
Such an initiative is also in line with the Operasi Semut movement by Indonesia Asri. This activity aims to educate the public about the importance of sorting and processing waste into items of economic value.
Interesting, isn’t it? You can take real steps by going to the field and educating the public about sorting waste. So, register now and be part of Indonesia Asri!
Read also: What Is Circular Economy? Here’s How Circular Economy Actions Benefit Our Environment








